Linear search is a method for finding a specific value in a list or array by iterating through each element in the list or array until the desired value is found. This method is also known as a sequential search. It is a simple search algorithm that is easy to understand and implement.
The basic idea behind linear search is to start at the first element in the list or array and compare it to the desired value. If the element is not the desired value, the algorithm moves on to the next element and continues this process until the desired value is found or the end of the list or array is reached.
One advantage of linear search is that it is easy to implement and understand, making it a good choice for small lists or arrays. Additionally, linear search does not require any pre-processing of the data and can be applied to any data type.
However, the main disadvantage of linear search is its time complexity. The time it takes to find a specific value in a list or array using linear search is directly proportional to the size of the list or array. For large lists or arrays, the search can take a significant amount of time.
One way to improve the time complexity of linear search is to implement a more efficient search algorithm, such as binary search. Binary search works by repeatedly dividing the list or array in half and eliminating half of the remaining possibilities with each iteration. This results in a time complexity of O(log n) which is much faster than linear search.
In practice, linear search is used in simple cases where the number of elements is small and or the data is not sorted, and the data is not large.
Another variation of linear search is known as a sentinel linear search, in which the last element of the array is replaced with the value being searched for. This eliminates the need to check if the end of the array has been reached and can improve the performance of the search.
Linear search is a basic search algorithm that is easy to understand and implement, but it can be slow for large lists or arrays. More efficient search algorithms, such as binary search, should be used when the number of elements is large and the data is sorted.
PSEUDO CODE:
This is a basic implementation of the linear search algorithm. It takes a list and an item to search for as its inputs. The function iterates through each element in the list using a for loop, starting at the first element and ending at the last element. If the current element is equal to the item being searched for, the function returns the index of that element. If the end of the loop is reached and the item has not been found, the function returns None.
Linear search is a simple algorithm to find an item in a list by checking every element in the list one by one. It's time complexity is O(n).
PYTHON CODE:
Here is an example of linear search implemented in Python:
The function takes in two arguments, the list arr and the value x to search for. Inside the for loop, the function checks if each element of the list is equal to x. If a match is found, the function returns the index of that element. If the end of the loop is reached without finding a match, the function returns -1.
In the example above, the function is called with an example list arr and the value x to search for. The result of the function call is then checked and the appropriate message is printed to the console.
JAVA CODE:
Here is an example of linear search implemented in Java:
In this example, the search() method takes in two arguments, an array arr and an integer x to search for. Inside the for loop, the method checks if each element of the array is equal to x. If a match is found, the method returns the index of that element. If the end of the loop is reached without finding a match, the method returns -1.
In the main() method, the example array arr and the value x to search for are defined. The search() method is called with these arguments and the result is stored in the variable result. The result of the function call is then checked and the appropriate message is printed to the console.
C CODE:
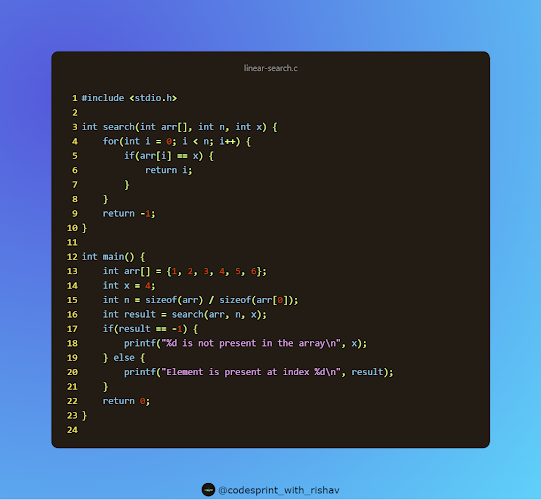
Here is an example of linear search implemented in C:
In this example, the search() function takes in three arguments, an array arr, an integer n representing the size of the array and an integer x to search for. Inside the for loop, the function checks if each element of the array is equal to x. If a match is found, the function returns the index of that element. If the end of the loop is reached without finding a match, the function returns -1.
In the main() function, the example array arr and the value x to search for are defined. The size of the array is calculated and passed as an argument to the search() function. The function is called with these arguments and the result is stored in the variable result. The result of the function call is then checked and the appropriate message is printed to the console.
C++ CODE:
Here is an example of linear search implemented in C++:
In this example, the search() function takes in three arguments, an array arr, an integer n representing the size of the array and an integer x to search for. Inside the for loop, the function checks if each element of the array is equal to x. If a match is found, the function returns the index of that element. If the end of the loop is reached without finding a match, the function returns -1.
In the main() function, the example array arr and the value x to search for are defined. The size of the array is calculated and passed as an argument to the search() function. The function is called with these arguments and the result is stored in the variable result. The result of the function call is then checked and the appropriate message is printed to the console.
JAVASCRIPT CODE:
Here is an example of linear search implemented in JavaScript:
In this example, the linearSearch() function takes in two arguments, an array arr and an element x to search for. Inside the for loop, the function checks if each element of the array is equal to x. If a match is found, the function returns the index of that element. If the end of the loop is reached without finding a match, the function returns -1.
In the example above, the function is called with an example array arr and the value x to search for. The result of the function call is then checked and the appropriate message is printed to the console.





Marvelous sir
ReplyDeleteExplanation superb
Glad you liked this one
Delete